Page 196 - SUSTAINABILITY ISSUES & COVID-19
P. 196
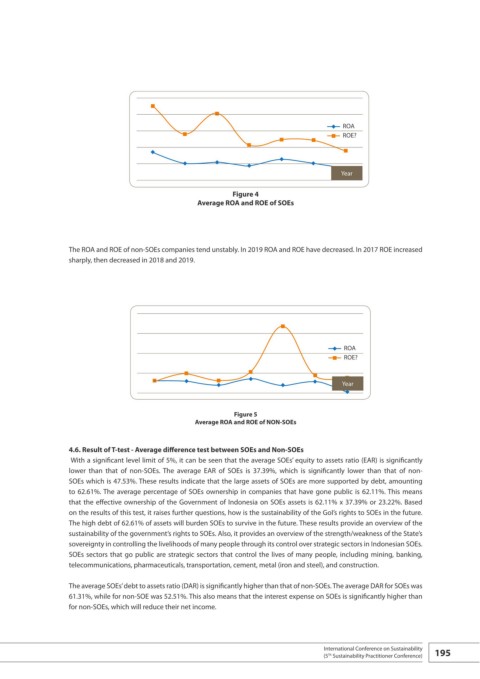
ROA
ROE?
Year
Figure 4
Average ROA and ROE of SOEs
The ROA and ROE of non-SOEs companies tend unstably. In 2019 ROA and ROE have decreased. In 2017 ROE increased
sharply, then decreased in 2018 and 2019.
ROA
ROE?
Year
Figure 5
Average ROA and ROE of NON-SOEs
4.6. Result of T-test - Average difference test between SOEs and Non-SOEs
With a significant level limit of 5%, it can be seen that the average SOEs’ equity to assets ratio (EAR) is significantly
lower than that of non-SOEs. The average EAR of SOEs is 37.39%, which is significantly lower than that of non-
SOEs which is 47.53%. These results indicate that the large assets of SOEs are more supported by debt, amounting
to 62.61%. The average percentage of SOEs ownership in companies that have gone public is 62.11%. This means
that the effective ownership of the Government of Indonesia on SOEs assets is 62.11% x 37.39% or 23.22%. Based
on the results of this test, it raises further questions, how is the sustainability of the GoI’s rights to SOEs in the future.
The high debt of 62.61% of assets will burden SOEs to survive in the future. These results provide an overview of the
sustainability of the government’s rights to SOEs. Also, it provides an overview of the strength/weakness of the State’s
sovereignty in controlling the livelihoods of many people through its control over strategic sectors in Indonesian SOEs.
SOEs sectors that go public are strategic sectors that control the lives of many people, including mining, banking,
telecommunications, pharmaceuticals, transportation, cement, metal (iron and steel), and construction.
The average SOEs’ debt to assets ratio (DAR) is significantly higher than that of non-SOEs. The average DAR for SOEs was
61.31%, while for non-SOE was 52.51%. This also means that the interest expense on SOEs is significantly higher than
for non-SOEs, which will reduce their net income.
International Conference on Sustainability 195
(5 Sustainability Practitioner Conference)
Th